Comprehensive Gene Expression Analysis and Neurotoxicity Testing of Human iPSC-derived Neural Progenitor Cells and Neurons
Society of Toxicology 2018
San Antonio, Texas, United States
March 12, 2018Abstract
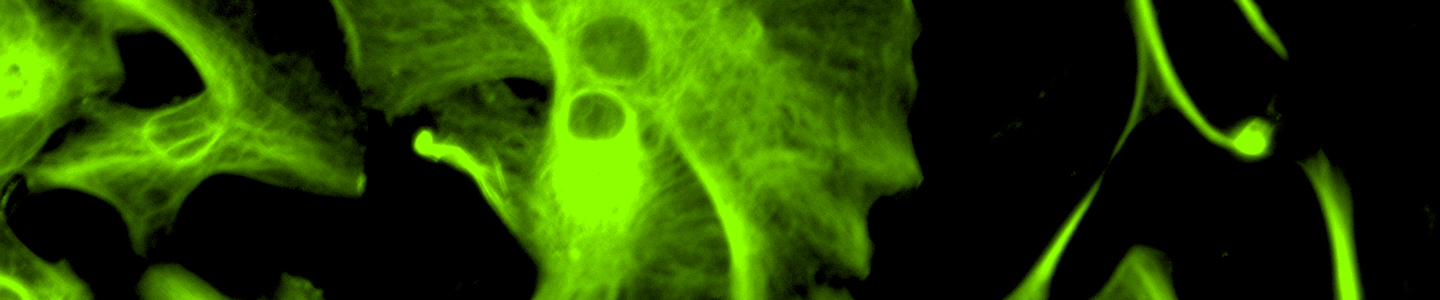
Human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC)-derived neural progenitor cells (NPCs) and neurons are an attractive in vitro model to study neurological development, neurotoxicity and to model diseases. However, there is a lack of validated normal and Parkinson’s NPCs and media that support differentiation into multiple types of neurons for disease modeling, drug screening, and toxicity screening.
Here, we investigated the expression of genes associated with the differentiation of NPCs during 3 weeks in dopaminergic differentiation media. Expression of both Tuj1 early neuron and TH dopaminergic neuronal genes was significantly increased in a time-dependent manner (p < 0.05) in 3 types of NPCs tested. Furthermore, expression of genes associated with glutamatergic (vGLUT2 and GLS2) and GABAergic (GABA) neurons was also increased in a time-dependent manner (p < 0.05) in 2 types of normal NPCs (ATCC ACS-5003 and ATCC ACS-5007) while expression of these genes was induced and peaked at the end of 2 weeks in Parkinson’s NPCs (ATCC ACS-5001). This shows that our NPCs and dopaminergic differentiation media are capable of producing GABAergic and glutamatergic neurons, in addition to dopaminergic neurons. Noticeably, there was significant induction of motor neuron gene (LIM3) expression in ACS-5003 and ACS-5001 NPCs, but not in ACS-5007 NPCs while there was significant induction of cholinergic (ChAT) neuron gene expression in ACS-5007 and ACS-5001 NPCs, but not in ACS-5003 NPCs during dopaminergic differentiation.
To validate that our NPCs and dopaminergic neuron differentiation media are suitable for drug screening, we conducted neurotoxicity screenings in 3 types of NPCs and NPCs-derived neurons using Reliablue cell viability reagent (ATCC 30-1014) assay and high content imaging analysis. We found that paclitaxel and vincristine significantly induced neurotoxicity (p < 0.001) in both ACS-5003 and ACS-5001 NPCs while piperine didn’t induce any significant neurotoxicity in all types of NPCs tested. Furthermore, amiodarone and chlorhexidine at 10 or 100 μM significantly decreased cell viability (p < 0.001) in both ACS-5003 and ACS-5001 NPCs. Cisplatin and hydroxyurea at 100 μM significantly induced neurotoxicity in ACS-5003 NPCs, but not in ACS-5001 NPCs. Furthermore, paclitaxel didn’t induce any significant neurotoxicity in both ACS-5003 and ACS-5007 NPCs-derived neurons by high content imaging analysis although it was toxic to NPCs with a IC50 of ~1 μM.
This study demonstrates that our iPSC-derived NPCs and dopaminergic differentiation media are suitable for studying neurological development and neurotoxicity screening.
Download the poster to explore the use of iPSC-derived NPCs in neurological development research.
Download